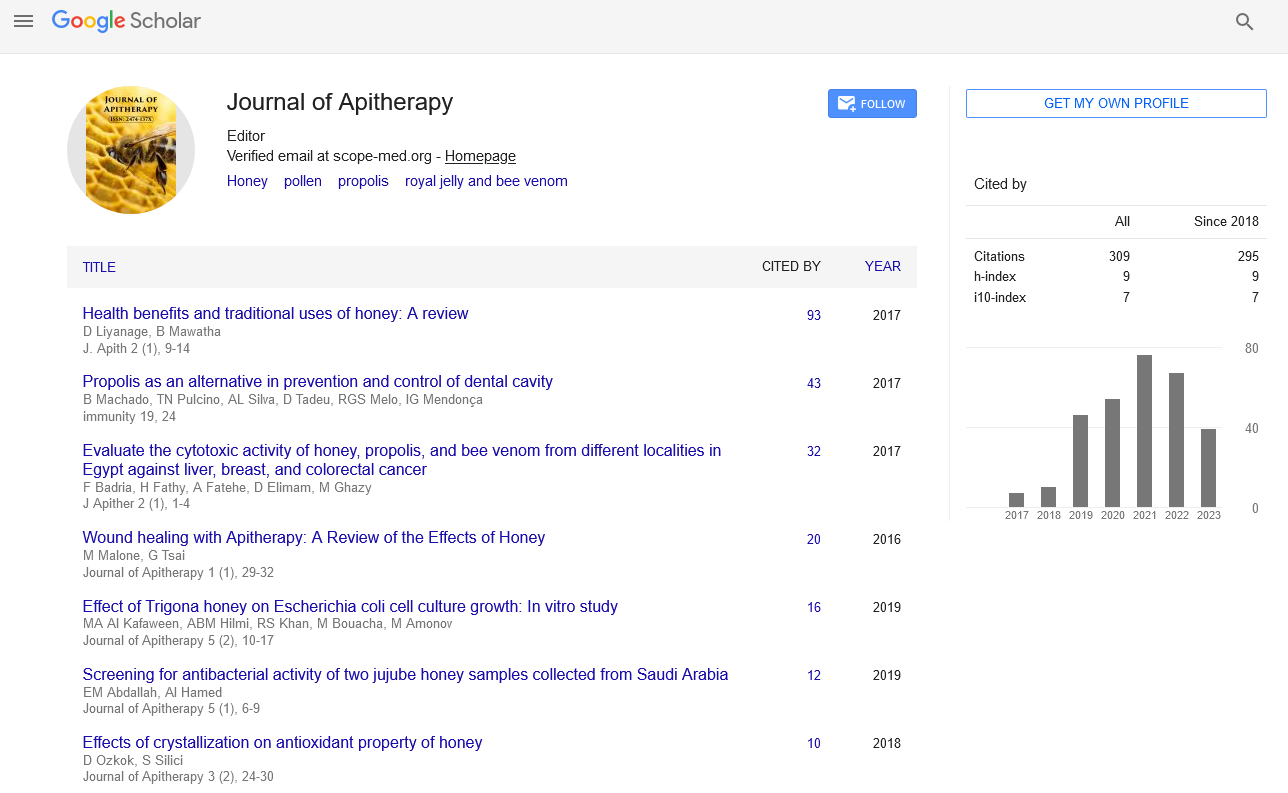
Perspective - Journal of Apitherapy (2022)
Bee Venom: Health Benefits, Side Effects, Uses
Ghada Mansour*Ghada Mansour, Department of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology, Zagazig University, Zagazig, Egypt, Email: ghadahassan@gste.sci.cu.edu.eg
Received: 15-Mar-2022, Manuscript No. JAPITHERPAY-22-61794; Editor assigned: 17-Mar-2022, Pre QC No. JAPITHERPAY-22- 61794 (PQ); Reviewed: 01-Apr-2022, QC No. JAPITHERPAY-22- 61794; Revised: 06-Apr-2022, Manuscript No. JAPITHERPAY-22- 61794 (R); Published: 15-Apr-2022
Description
Bees produce bee venom. This is the venom that causes bee stings to hurt. Bee venom is occasionally utilised in medicine. Bee venom should not be confused with bee pollen, honey, propolis, or royal jelly. A dose of bee venom is administered to people who are allergic to bee stings. It’s also used to treat osteoarthritis, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, nerve pain, and other ailments, but there’s no scientific proof to back up these claims. When injected under the skin by a competent medical professional, bee venom is generally harmless for most people. Some patients may experience redness and edoema around the injection site. Itching, anxiety, difficulty breathing, chest tightness, heart palpitations, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, tiredness, confusion, fainting, and low blood pressure are some of the possible side effects. People with the most severe allergy to bee stings, people treated with honeybee venom, and women are more likely to experience side effects. Under medical supervision, live bee stings have been successfully provided in amounts up to 20 bee stings three times weekly for up to 24 weeks.
Giving the immune system repeated and controlled injections of bee venom under the skin helps the immune system become accustomed to bee venom and reduces the severity of a bee venom allergy. In those with severe allergies to bee stings, a series of bee venom shots under the skin bee venom immunotherapy appears to be beneficial in lowering reactions to bee stings. Immunotherapy with bee venom gives 98 percent to 99 percent protection against bee sting reactions. When immunotherapy is halted, the likelihood of a reaction increases to roughly 5% to 15% over the next 5 to 10 years. The FDA has cleared the use of purified bee venom for injection under the skin.
Early research suggests that dilute bee venom injections may help people with frozen shoulder pain and disability. However, it does not appear to increase range of motion. In addition, very dilute bee venom injects do not appear to be effective. The early study on bee venom as a treatment for osteoarthritis is conflicting. Injecting bee venom into the skin at certain places in the knees and back may improve pain and function in persons with osteoarthritis of the knee, according to a comprehensive research.
Parkinson’s disease is a neurological disorder. Dilute bee venom injections may help persons with Parkinson’s disease, according to preliminary study. However, if the amount of bee venom is too low, it may not be effective. When administered under the skin by a competent medical expert at authorised quantities, bee venom is possibly safe during pregnancy and breast-feeding. Although no adverse effects have been recorded at standard doses, some healthcare professionals reduce the maintenance dose by half during pregnancy. High dosages of bee venom are possibly unsafe during pregnancy because they can cause the uterus to contract by increasing the release of a molecule called histamine. This could result in a miscarriage. If you’re pregnant, stay away from heavy amounts of bee venom. The immune system may be boosted by bee venom. Because bee venom boosts the immune system, it may reduce the effectiveness of immune-suppressing drugs.
Copyright: © 2022 The Authors. This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/). This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.