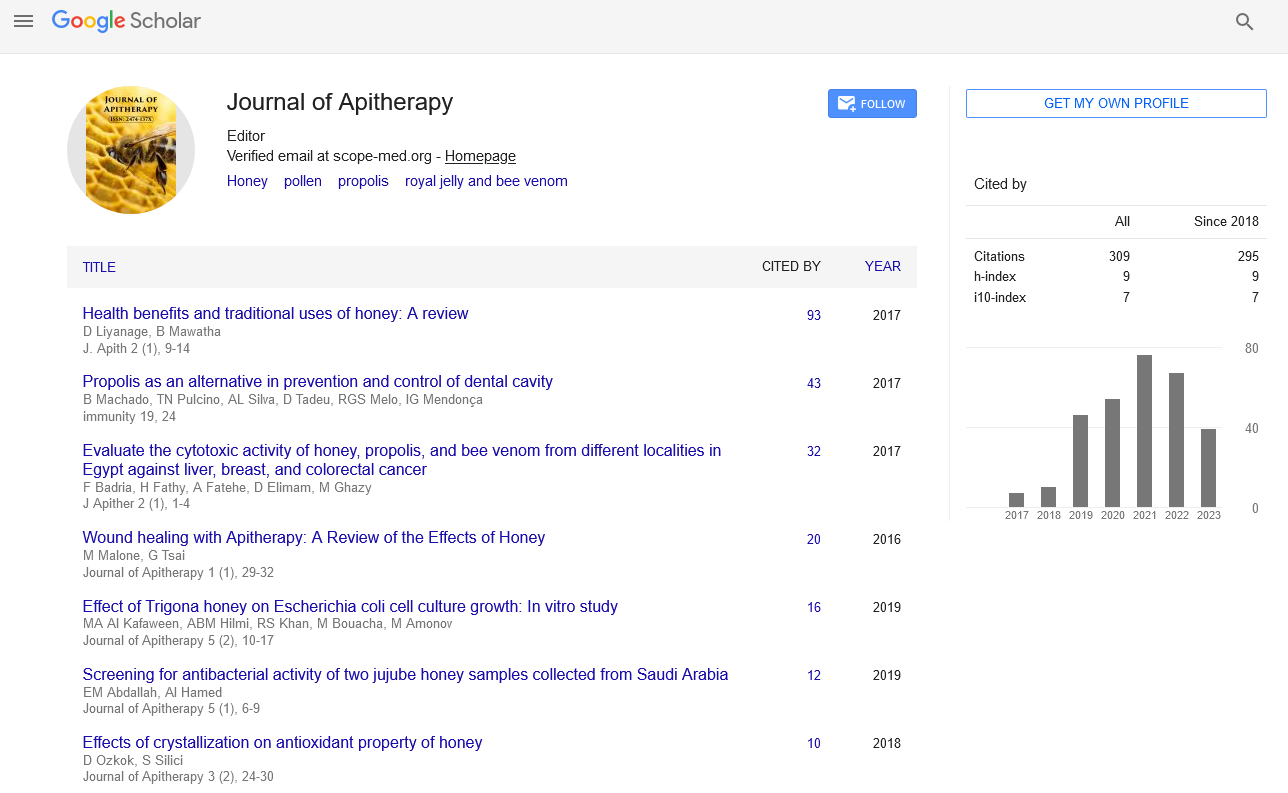
Mini Review Article - Journal of Apitherapy (2023)
Aroeira Honey: New Product for Apitherapy
Vanessa de Andrade Royo1*, Júlia de Sousa Cordeiro1, Pedro Henrique Fonseca Veloso1, Elytania Veiga Menezes1, Dario Alves de Oliveira1, Afrânio Farias de Melo Júnior1 and Luciano Fernandes de Souza22Department of Apiculture, Cooperative of Beekeepers and Family Farmers of Northern Minas organization, Minas Gerais, Brazil
Vanessa de Andrade Royo, Department of General Biology, State University of Montes Claros (Universidade Estadual de Montes Claros), Montes Claros, Brazil, Email: vanroyo31@gmail.com
Received: 20-Oct-2023, Manuscript No. JAPITHERAPY-23-117789; Editor assigned: 23-Oct-2023, Pre QC No. JAPITHERAPY-23-117789 (PQ); Reviewed: 07-Nov-2023, QC No. JAPITHERAPY-23-117789; Revised: 14-Nov-2023, Manuscript No. JAPITHERAPY-23-117789 (R); Published: 21-Nov-2023
Abstract
It is known that honey has been used since ancient times in folk medicine to treat illnesses. The antimicrobial action and antioxidant capacity, the high levels of phenolic compounds, have aroused the interest of the scientific community. In addition to the biological activities reported for this honey, such as anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antioxidant, among others. The Geographical Indication (GI) of aroeira honey allowed the recognition and added value to the product and regional beekeeping production. This article presents a conglomerate of information about Aroeira honey, a mixed honey of floral honey and melate, produced by the bee Apis mellifera L, the psyllid Tainaires myracrodruon and the botanical species Astronium urundeuva.
https://blogum.blogaaja.fi/
https://blogum-1.jimdosite.com/
https://blogummm.edublogs.org/
https://blogummm.websites.co.in/
https://blogum18.wordpress.com/
https://benim-blogum.jigsy.com/
https://fuiegs-symbeaurds-build.yolasite.com/
https://blogum-03.webselfsite.net/
https://blogummm.mystrikingly.com/
https://blogum.splashthat.com/
https://blogum3.webnode.com.tr/
https://blogum.odoo.com/
https://blogum.creatorlink.net/
https://whiteseotr1-s-site.thinkific.com/enrollments
https://blogum.estranky.cz/
https://653ba4fbb538c.site123.me/
https://blogum12m.blogspot.com/
https://blogum.hashnode.dev/
https://whiteseoturkey1.wixsite.com/blogum
https://sites.google.com/view/blogummm/
https://codepen.io/blogum
https://blogumm.livejournal.com/
https://wakelet.com/@blogum82816
https://www.homify.com/users/9538383/blogum
https://lessons.drawspace.com/profile/323613/blogum
https://my.desktopnexus.com/blogum/
https://writeupcafe.com/profile/BLOGUM/
https://www.pearltrees.com/blogum
https://www.easyfie.com/blogum
https://pharmahub.org/members/27615/profile
https://www.zupyak.com/u/blogum/posts
https://www.metroflog.co/blogum
https://www.fuzia.com/fz/blogum-blogum
https://tr.pinterest.com/blogum12/
https://my.getjealous.com/blogum
https://micro.blog/blogum
https://www.tumblr.com/blogummm
https://hub.docker.com/u/blogum
https://fire.blogfree.net/?act=Profile&MID=1342323
https://blogum.pixnet.net/blog
https://www.threadless.com/@blogum/activity
https://blogum.neocities.org/
https://blogum12.amebaownd.com/
https://teletype.in/@blogum
https://ubl.xml.org/users/blogum
https://educatorpages.com/site/blogum/
https://blogum.onlc.fr/
Keywords
Antimicrobial action; Antioxidante capacity; Biological activities; Melate; Psyllid; Bee
Introduction
Natural product of high nutritional quality, produced by bees from the nectar present in flowers, secretions from living parts of plants, or from sap-sucking insects. Rich in sugars, fructose and glucose, it is formed through enzymatic synthesis and possesses high energy value. Consumed worldwide, it has become important for human health due to its various biological properties, such as healing, soothing, wound healing, stimulating, among others [1]. Numerous substances present in honey are responsible for its qualifications, which is why it has been used since ancient times in folk medicine to treat various diseases. Greeks and Egyptians topically applied honey to the skin to treat wounds and burns [2]. Celsius, in the Christian era, believed that honey has agglutinating properties on wounds [3].
According to their origin, honey can be classified as extrafloral (honeydew) or floral. Extrafloral honeys consist of different floral sources, while honeydew honey is obtained through secretions from living parts of plants or excretions of sap-sucking insects, as is the case with aroeira honey. Floral honey is obtained from the nectar of flowers and can be classified as monofloral or multifloral [4]. However, the chemical composition depends on various factors that influence the composition, such as botanical origin, soil type, and time of year, region where they are collected and produced, among others [5].
Literature Review
Aroeira honey
The aroeira honey produced in the North of Minas Gerais has antimicrobial, antioxidant, and gastrointestinal properties, with a less sweet taste and the unique characteristic of never crystallizing at room temperature. It is a mixed honey of honeydew and floral nectar, obtained through secretions from living parts of plants or excretions of sap-sucking insects. The production period is characterized by low floral availability, high temperatures, and low humidity. This combination of factors makes flowers scarce during the dry season, leading bees to seek aroeira as a viable alternative for honey production [6].
The aroeira trees shed their leaves during the dry season, and to protect themselves from the sun’srays, they utilize sap-sucking insects (psyllids -Tainaires myracrodruon) [7]. By feeding on the trees, thepsyllids induce the aroeira to produce phenolic compounds, which are expelled by the plant and used as a natural sunscreen. These insects, in turn, feed on the sap enriched with phenolic compounds and release a sugary substance known as honeydew. Bees then collect this sugary substance, mixed with phenolic secretions and excretions from the psyllids, to produce honey [6]. Aroeira honey from North Minas Gerais consists of the flowering of the aroeira tree and honeydew from these insects, making it an exclusive product of the region. This honey should be harvested immediately after the flowering of Astronium urundeuva to ensurethe purity of the monofloral honey [8].
Hence, honey becomes an interaction between thearoeira tree (Astronium urundeuva) and the psyllid (Tainaires myracrodruon). The sap sucked by the psyllid undergoes digestion and maturation within its organism, resulting in the excretion of a sugary substance that stimulates the aroeira to produce secondary metabolites, particularly phenolic compounds. This process imparts peculiar characteristics to the honey, such as its dark amber color, a feature that, for a long time, rendered the product of low commercial value. Often, beekeepers would maintain honey stocks until the following harvest season [9].
Thus, it possesses distinctive characteristics such as high levels of invertase and the presence of melezitose and erlose, high density, dark amber color, elevated electrical conductivity, high ash content, lower acidity, and a high concentration of phenolic compounds uncommon in any other type of honey. Research conducted in collaboration with the Ezequiel Dias Foundation (FUNED) highlighted the honey’s antibacterial activity against Helicobacter pylori, the etiological agent of gastritis, stomach cancer, and gastric ulcers [9,10].
In 2020, the application for the registration of Geographical Indication for Aroeira honey from North Minas was submitted to the National Institute of Industrial Property (NIIP). This involved a preliminary survey with a bibliographic and documentary search, followed by an assessment of the registration status of the Council for the Development of Apiculture in North Minas (CODEANM) and the requirements for intellectual property protection.
Subsequently, questionnaires and interviews were conducted with CODEANM members, as well as government and private entities involved [11].
In studies conducted, the results from color determination indicate that the evaluated aroeira honeys exhibited a dark amber hue, similar to Manuka honey. Analyses for phenolic and flavonoid content were higher or equal to those found in the literature for other honeys, regarding the assessment of antioxidant capacity [5].
Discussion
Antioxidant capacity
Antioxidants are substances closely linked to the protection and prevention of the cellular oxidation process, with the ability to eliminate and inhibit the action of free radicals. They are substances present in foods, especially derived from plants [12]. Honey, being essentially derived from plants, whether from floral nectar, sap-sucking insects, or a mixture of these sources, carries secondary metabolites, such as phenolic compounds, which have the ability to donate electrons and stabilize free radicals. Studies report variations in the antioxidant activity of aroeira honeys in the assay of antioxidant capacity conducted with 2, 2-Diphenyl-1-Picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), as can be seen in Table 1.
| Honey | Botanical origin | Country | *CE50 mg 100 g-1 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aroeira | Astronium urundeuva (Anacardiaceae) | Brazil | 15.00 ± 0.07 | [5] |
| Aroeira | Astronium urundeuva (Anacardiaceae) | 11.30 ± 0.05 | ||
| Aroeira | Astronium urundeuva (Anacardiaceae) | 30.31 ± 0.06 | ||
| Aroeira | Astronium urundeuva (Anacardiaceae) | 20.30 ± 0.26 | ||
| Aroeira | Astronium urundeuva (Anacardiaceae) | 18.36 ± 0.15 | ||
| Aroeira | Astronium urundeuva (Anacardiaceae) | Brazil | 68.81 ± 2.36 | [13] |
Note: *: Concentration effective.
High levels of phenolics have been reported for aroeira honey, as documented by Pena-Junior et al. [5] at 76.83 ± 15.26 mgGAE 100 g-1, Gardoni et al. [14] at 142.5 ± 22.6 mg 100 g-1, and Royo et al. [13] at 74.74 ± 0.12 mgGAE 100 g-1. This aligns with the results described for the antioxidant activity found in the literature for aroeira honey.
A recent study utilized a phenolic-rich aroeira honey extract obtained through the recovery process of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) system. The results obtained for antioxidant activity showed an EC50 value of 701.5 ± 12.00 µg/mL [15]. This value is higher than those reported in the literature, which analyzed aroeira honey in the form of an extract or in a hydroalcoholic solution composed of honey and 70% alcohol.
Biological activities
Honey is attributed with numerous biological activities, such as antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antioxidant, antidiabetic, anti-obesity, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and wound-healing properties, in addition to effects on cardiovascular, nervous, and respiratory systems [16]. Due to the reported biological activities of honey, this product becomes highly sought after and consumed by individuals seeking alternative therapies, as well as a functional food.
Specifically for aroeira honey, antibacterial activityagainst Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus hasbeen reported [17], as well as antitumor effects [15], antifungal properties [18], antiacetylcholinesterase properties [19] and the presence of phenolic compounds and flavonoids [5]. The described properties of this type of honey make it a product that can be used in conjunction with other therapies. The use of honey as a medicinal product dates back to antiquity, with variousforms of application. Aroeira (Astronium urundeuva) isa medicinal plant used in the Brazilian Cerrado, with indications for its anti-inflammatory, antiulcerogenic [20], antiseptic, wound-healing, antifungal, and antimicrobial properties [21].
Through research, the anti-inflammatory and antibiotic action against the Helicobacter pylori bacteria, acausative agent of stomach problems such as stomach cancer, gastritis, and ulcers, has been demonstrated, along with a reduction in proliferation and migration of Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) cells [9]. This establishes its potential for the treatment of diseases and drug development. Additionally, a reduction in bacterial growth was observed for both Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, with the optimal concentrationfor inhibition being 3.125% (w/v). This highlights the therapeutic potential of aroeira honey produced in the North of Minas, contributing to the value addition and commercialization of this type of honey [17].
Conclusion
In conclusion, aroeira honey from the North of Minas Gerais, due to its origin involving the aroeira tree and sap-sucking psyllids, leads to the production of honey rich in phenolic compounds, with a distinct flavor pro file, and offers a unique and valuable combination of biological properties, such as antimicrobial and antioxidant. This honey not only possesses medicinal properties but also demonstrates the potential for drug development and as a complementary therapy for various diseases.
References
- Bizzaria DK, Filgueiras CT. Microbiological analysis of bee honey, consumed in the municipality of Campo Grande-MS. Hig. Alim 2003;17:104-105.
- Batiston TFTP. Antimicrobial activity of different stingless bee honeys. Universidade do Estado de Santa Catarina-UDESC 2017;1-85.
- da Silva RA, Maia GA, de Sousa PHM, Costa JC. Composition and therapeutic properties of bee honey. Food and Nutrition. Araraquara 2006;17(1):113-120.
- Technical regulation on the identity and quality of honey. Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Supply, Brasil.
- Pena Junior DS, Almeida CA, Santos MCF, Fonseca PHV, Menezes EV, de Melo Junior AF, et al. Antioxidant activities of some monofloral honey types produced across Minas Gerais (Brazil). Plos One 2022;17(1):e0262038.
- Demier ADM, de Oliveira DC, Makishi F. Sweet forests in the North of Minas Gerais: Actors, institutions and construction of the geographical indication of aroeira honey. Revista Espinhaço 2020;9(1):61-70.
- Aristides A. Aroeira honey: Properties, origin and differences. ECOA. 2023
- Calaça P, Schlindwein C, Bastos EMAF. Discriminating unifloral honey from a dioecious mass flowering tree of Brazilian seasonally dry tropical forest through pollen spectra: Consequences of honeybee preference for staminate flowers. Apidologie 2018;49:705-720.
- Bastos EMAF. Relato dos Resultados das Pesquisas com Mel de Aroeira. Vídeo Institucional. Belo Horizonte: FUNED. 2017.
- Bastos EMAF, Calaça PSST, Simeao CMG, da Cunha MR. Characterization of the honey from Myracrodruon urundeuva (Anacardiceae-Aroeira) in the dry forest of Northern of Minas Gerais/Brazil. Advances and Agricultural Science 2016;4(4):64-71.
- Spyer DC. The Geographical Indication by Designation of Origin of Aroeira Honey from the North of Minas. 2020
- Rahaman MM, Hossain R, Herrera‐Bravo J, Islam MT, Atolani O, Adeyemi OS, et al. Natural antioxidants from some fruits, seeds, foods, natural products, and associated health benefits: An update. Food Sci Nutr 2023;11(4):1657-1670.
- Royo VA, Oliveira DA, Veloso PHF, Sacramento VM, Olimpio ELA, Souza LF, et al. Physicochemical profile, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of honeys produced in Minas Gerais (Brazil). Antibiotics 2022;11(10):1429.
- Gardoni LCP, Santana RM, Brito JCM, Ramos LX, Araújo LA, Bastos EMAF, et al. Content of phenolic compounds in monofloral aroeira honey and in floral nectary tissue. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira 2022;57: e02802.
- Lima WG, da Silva Santos FR, de Faria VO, de Souza NA, de Souza-Costa LP, de Assis DCS, et al. Production of a phenolic-rich extract of aroeira honey and characterization of its antimicrobial, antitumoral and antioxidant activities. Revista Colombiana de Ciencias Químico-Farmacéuticas 2023;52(1):471-498.
- Al-Kafaween MA, Alwahsh M, Mohd Hilmi AB, Abulebdah DH. Physicochemical characteristics and bioactive compounds of different types of honey and their biological and therapeutic properties: A comprehensive review. Antibiotics 2023;12(2):337.
- Viana FR, do Carmo LS, Bastos EMAF. Antibacterial activity of aroeira honeys produced in Minas-Gerais against bacteria of clinical importance. Acta Sci Biol Sci 2018;40:1-4.
- Lima WG, Brito JCM, da Cruz Nizer WS, de Assis DCS. Antifungal, antibiofilm and anti-resistance activities of Brazilian monofloral honeys against Candida spp. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 2022;42:102335.
- Liberato MCTC, de Morais SM, Siqueira SMC, de Menezes JESA, Ramos DN, Machado LKA, et al. Phenolic content and antioxidant and antiacetylcholinesterase properties of honeys from different floral origins. J Med Food 2011;14(6):658-663.
- Souza SMC, Aquino LCM, Milach AC, Bandeira MAM, Nobre MEP, Viana GSB. Antiinflammatory and antiulcer properties of tannins from Myracrodruon urundeuva Allemão (Anacardiaceae) in rodents. Phytother Res 2007;21(3):220-225.
- Machado AC, Oliveira RC. Phytotherapeutic medicines in dentistry: Evidence and perspectives on the use of aroeira-do-sertão (Myracrodruon urundeuva Allemão). Rev Bras de Plantas Medicinais 2014;16(2):283-289.